Continuing Education Activity
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome, also known as Ritter disease is a disease characterized by denudation of the skin caused by exotoxin producing strains of the Staphylococcus species, typically from a distant site. It usually presents 48 hours after birth and is rare in children older than six years. It may also present in immunocompromised adults or those with severe renal disease. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and treating this condition.
Objectives:
- Identify the etiology of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome.
- Outline the appropriate evaluation of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome.
- List the treatment and management options available for Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome.
- Recognize the importance of a team based approach to management of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome that may involve emergency clinicians, pediatric clinicians, and wound/burn care clinicians, especially in severe cases.
Introduction
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome, also known as Ritter disease is a disease characterized by denudation of the skin caused by exotoxin producing strains of the Staphylococcus species, typically from a distant site. It usually presents 48 hours after birth and is rare in children older than six years. It may also present in immunocompromised adults or those with severe renal disease.[1]
The disorder is characterized by significant exfoliation of skin following cellulitis. The severity may vary from a few blisters to system exfoliation leading to marked hypothermia and hemodynamic instability.
Etiology
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome is caused by the epidermolytic exotoxin that is produced by some strains of Staphylococcus. There are at least two toxins that cause Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome. However, testing for the specific phage-type is not helpful or available. The disease usually follows a localized infection from the upper respiratory tract, ears, conjunctiva, or umbilical stump. In adults, it may result from an abscess, arteriovenous fistula infection, or septic arthritis, among others. Often a source cannot be identified. [1]
Children are at a greater risk because of the immature renal system lack of immunity and the absence of maternal antibodies in those who are not breastfed. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome may occur as an outbreak in daycares or nurseries. The majority of affected children are less than age 2.
Epidemiology
The incidence of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome is relatively low. A study in the Czech Republic showed an incidence of approximately 25 cases per 100,000 children younger than one year of age. Most cases occur in children younger than two years old. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome can occur in outbreaks, particularly in nurseries. It is far less common in adults. When they do occur, cases in adults typically involve those with immunosuppression such as HIV/AIDS, severe renal impairment or renal failure, or in those with malignancy.[2][1]
Pathophysiology
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome is caused by toxin-producing strains of Staphylococcus bacteria. These toxins target the desmoglein 1 complex in the zona granulosa of the epidermis, resulting in skin exfoliation. It can range from a mild localized form to exfoliation of the entire body. Those with previous antibodies are more likely to have the localized form. The resultant skin loss predisposes patients to hypothermia and a large volume fluid loss, as well as, the potential for additional or worsening infections. [1]
The exfoliative toxins target desmoglein, which is an important keratinocyte that plays a critical role in cell to cell adhesion. This protein is only found in the superficial epidermis. The relative concentration of desmoglein varies in the skin. It is believed that in patients with renal failure the exotoxins are not excreted and thus contribute to disease. Adults rarely develop the syndrome because of antibodies to the exotoxin. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome can be mistaken for bullous impetigo. Both cause blistering skin lesions caused by the staphylococcus exotoxin, but in the latter, the exotoxins remain localized to the site of infection. In staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, the exotoxins are spread via the systemic circulation to distant sites. Further staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome can be differentiated from toxic epidermal necrolysis by the fact the former is intraepidermal, whereas in TENS there is necrosis of the entire epidermal layer.
Histopathology
The biopsy will show the site of cleavage in the skin, which is superficial. In TEN, the site of cleavage is much deeper in the epidermis.
History and Physical
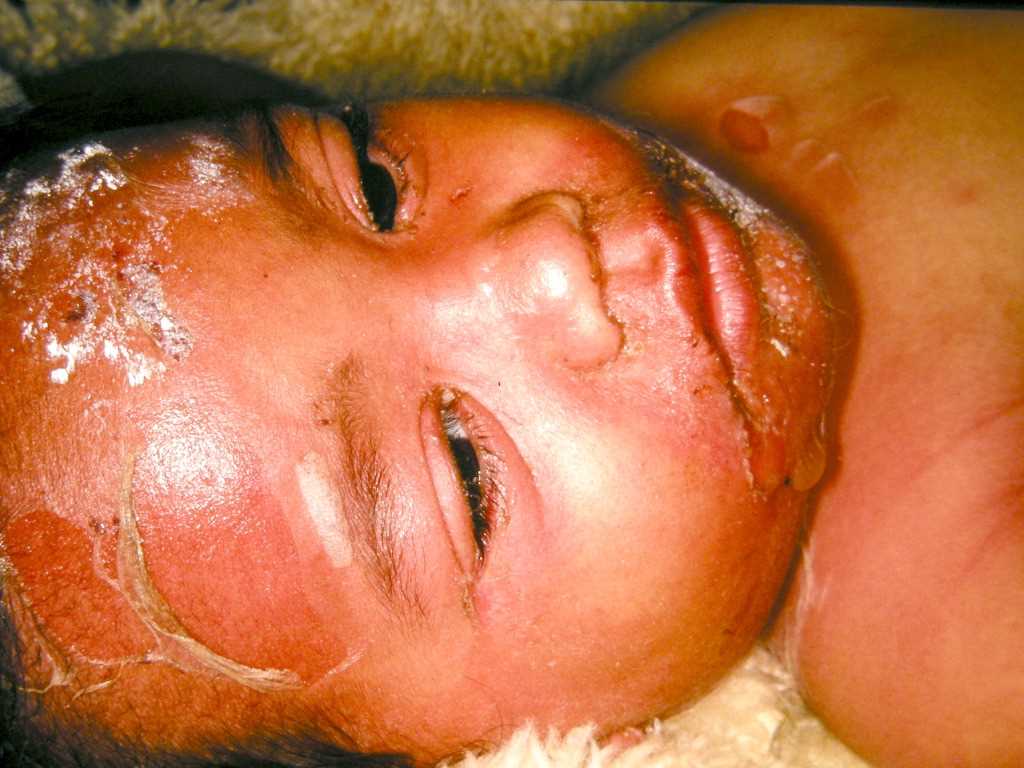
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome initially presents with irritability, fever, and malaise. Within 24 to 48 hours, a very tender rash develops. The rash typically starts on the face and flexures (groin, axillae, neck) with erythema and fissures. Soon after this, large thin blisters form. The characteristic flaccid, blisters and bullae contain anything from thin, sterile cloudy fluid to frank yellow pus underneath. Unlike scarlet fever, the rash of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome tends to be more tender, and the skin exfoliates.
The disease may present with only localized blisters. However, in its classic form, the disease progresses to a diffuse, markedly erythematous rash with significant tenderness. Further progression transitions to flaccid blisters and desquamation. Nikolsky’s sign is present. Patients may appear well or present with fulminant sepsis with hypotension and shock. There is typically no mucous membrane involvement with Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome, although they may be hyperemic. This can help in differentiating Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome from Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis, which does involve the mucosal surfaces. Skin typically heals within two weeks. [1]
Evaluation
Basic laboratory work up such as complete blood cell count (CBC) with differential and urinalysis (UA) should be obtained to assess for sepsis in any patient with more than the localized form of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome. Electrolytes should be checked if dehydration is suspected. Blood cultures and cultures of blister fluid are typically negative. However, in critically ill patients, cultures and sensitivities from any potential source should be obtained to determine the source of infection. Culture from the site of suspected primary infection is warranted. A skin biopsy or frozen section of a blister roof can be very helpful, as it will aid in diagnosis and to help differentiate from other conditions such as toxic shock syndrome or other vesiculobullous diseases. [1]
A chest x-ray should be done to rule out an infectious process in the lungs as a source of infection.
Treatment / Management
Antibiotics covering staphylococcus should be administered early and include Cefazolin, Nafcillin or Oxacillin for methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). Vancomycin should be administered if methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is suspected, especially in those with recent healthcare exposure or in areas with a high prevalence of MRSA. Topical antibiotics alone are not effective, and even localized Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome should be treated with systemic antibiotics. If concern for a secondary bacterial skin infection arises, additional antibiotics with pseudomonas coverage should be started. Intravenous (IV) fluids should be administered in those with signs of dehydration or and/or sepsis. [3][1]
Emollients and non-adherent dressings should be applied to the skin and denuded areas to promote healing and reduce heat loss. Supportive care including management of dehydration, temperature regulation, and nutrition is of critical importance. Patients with significant skin involvement are prone to hypothermia and fluid loss due to the loss of the epidermis. The application of silver sulfadiazine should be avoided given the potential for increased systemic absorption and resultant toxicity. [4]
Those with very mild, localized disease may be discharged home on oral antibiotics and close follow-up with their primary care physician, though more severe cases should be admitted. Severe cases may benefit from admission to a burn unit when possible. Patients with Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome should be isolated from others to prevent further infections and outbreaks. Hand hygiene with contact isolation and proper cleaning of objects such as stethoscopes are important in preventing additional outbreaks in hospitals. Potential carriers of toxin-producing strains of staph aureus should be identified and treated to prevent outbreaks. Those caring for the patient should undergo nasal swab testing for S. aureus and be treated if positive.
Those patients who are recognized early and treated appropriately overall have a very good prognosis. The mortality rate in children is less than 5%. Within a few days of treatment, fevers subside, and the rash begins to improve. Skin desquamation usually occurs within five days with complete resolution within two weeks, typically without any permanent sequelae. In adults, however, the mortality rate is much higher, up to 59% in one study. [1]
Differential Diagnosis
- Bullous Impetigo
- Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Scarlet Fever
- Kawasaki Disease
- Cellulitis
- Impetigo
- Thermal Burn
- Stevens Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
- Epidermolysis Bullosa [5]
Prognosis
Generally, pediatric patients do well with minimal to no scarring, and healing typically occurs within 2 weeks. The mortality rate in children is <5%. Adults have much higher mortality, as high as 60%. [1][6]
Complications
Complications include dehydration, secondary infections, electrolyte imbalance, sepsis, renal failure, and scarring.[7]
Consultations
Consultation with a Dermatologist should be considered if the diagnosis is uncertain. Burn Centers and/or Burn Physicians should be consulted in severe cases.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
It is important to approach the diagnosis and management of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome as a team, particularly with unclear cases. Expert consultation with Dermatologists can help eliminate alternative diagnoses and guide treatment.
There is typically no mucosal involvement in Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome which may help differentiate it from Scarlet Fever, Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) which all involve mucous membranes. The demographics of these diseases also tend to be different, as Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome is more common in neonates, whereas TSS, for example, tends to occur in patients using tampons, nasal packing, as well as, those who have had recent surgery. Colonized caregivers and those with patient contact require treatment with Chlorhexidine, and nasal carriers should be treated with topical mupirocin. The mortality is relatively low in children when appropriate treatment is initiated, but it is much higher in adults even with appropriate antibiotic and supportive therapy. [8][1][9][10]
In severe cases, referral to a burn center with experts in wound care should strongly be considered in order to reduce fluid losses and prevent scarring. Primary care clinicians including nurses should immediately consult with a dermatologist if there is doubt about the diagnosis. The earlier the treatment, the better the outcomes. Close communication between the team members is vital is one wants to improve outcomes.