Introduction
Pulmonary compliance, a measure of the expansion of the lung, is critical to the proper function of the respiratory system. Lung compliance can be calculated by dividing volume by pressure. Factors affecting lung compliance include elasticity from the elastin in connective tissue and surface tension, which is decreased by surfactant production. Lung compliance participates in the lung-chest wall system by opposing the outward pull of chest wall compliance. The net compliance (lung-chest wall system) allows the lungs to achieve appropriate functional residual capacity, the volume remaining after passive expiration.
Cellular Level
Anatomically, the respiratory tract divides into two zones: the conducting zone and the respiratory zone. These two zones of the lung contain different cells to support the specialized functions of the respective regions. The conduction zone conditions and facilitates the movement of air entering the lungs. This zone mostly contains a respiratory epithelium that is ciliated or pseudostratified columnar. This dominating cell type helps moisturize and filter the air. The five types of specialized cells in the conducting zone include ciliated cells, goblet cells, basal cells, brush cells, and neuroendocrine cells.[1][2][3]
- Ciliated cells: most plentiful cell types and functions to remove debris.[4]
-
Goblet cells: trap and destroy micro-particles by mucin granules. This cell type decreases in number down the respiratory tree and eventually becomes replaced with club cells.[3]
-
Basal cells: connects ciliated and goblet cells to the basement membrane.[5]
-
Brush cells (also known as type 3 pneumocytes): Columnar or pear-shaped cells with microvilli and unmyelinated nerve ending throughout a small portion of the mucosal epithelium. The function is uncertain. However, some literature indicates a possible chemoreceptor function that monitors air quality.[6]
-
Neuroendocrine cells (also known as Kulchitsky cells): located in the bronchial submucosa and secretes catecholamines and polypeptide hormones (serotonin, calcitonin, and gastrin-releasing factor).[3]
The respiratory zone includes the alveolar epithelium, which has a lining with three types of pneumocytes.
- Type 1 Pneumocytes: squamous cells line the majority of alveolar surfaces to promote optimal gas diffusion.[7]
- Type 2 Pneumocytes: secrete pulmonary surfactant, which ultimately decreases alveolar surface tension to prevent alveolar collapse as well as decreasing elastance and increasing compliance. These cells are precursors to type-1 cells and other type-2 cells. This ability to proliferate makes type 2 pneumocytes helpful during lung damage.[7]
- Club cells (previously known as Clara cells): nonciliated, low-columnar/cuboidal cells with secretory granules. Club cells secrete part of the surfactant, degrade toxins, and also act as regional progenitor cells in conditions of lung damage.[8]
Development
The endoderm gives rise to the epithelial layer of the lungs, while the mesoderm gives rise to the connective tissue. Lung development subdivides into five distinct stages: embryonic (weeks 4 to 7), pseudo glandular (week 5 to 7), canalicular (week 16 to 25), saccular (week 26 to birth), and alveolar (week 36 to8 years).[9][3][10]
Embryonic Stage: Development of the lungs begins in the fourth week: lung buds stem from the distal end of the respiratory diverticulum. The respiratory diverticulum forms from the ventral foregut. The two lung buds further divide into two bronchial buds. In week five, bronchial buds branch off into main (primary) bronchi. By the end of the embryonic stage, lobar (secondary) and segmental (tertiary) bronchi have also branched off. Simultaneously, two pulmonary arteries grow from the sixth aortic arch, which will later form a vascular plexus.[3][10][11][10]
Pseudoglandular Stage: Between week five and sixteen, terminal bronchioles and surrounding capillary network forms. After the terminal bronchi mark the end of the development for the conducting zone and the beginning of the respiratory zone, which includes the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs. Moreover, mesenchymal cells differentiate into cartilage and smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells, as well as fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and endothelial cells, are known to produce elastin.[3][10][12][10]
Canalicular Stage: Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and a stronger capillary network develop between weeks sixteen and twenty-five. Alveolar ducts support the growth of lung parenchyma that acts as the site for gas exchange. Additionally, airways develop during this stage, and pneumocytes (type 1 and 2) develop at twenty weeks.[3][10]
Saccular Stage: Alveolar ducts branch off into terminal sacs between week twenty-six and birth. The increase of fetal cortisol during this stage also leads to maturation of lungs (tissue remodeling and cell differentiation) as well as synthesis and secretion of surfactant. More specifically, the maturation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a critical event that leads to proper lung compliance. During ECM maturation, stability takes place through elastin and collagen cross-linking.[3][10][13]
Alveolar Stage: Alveoli continue to develop and proliferate after birth to about eight years of age.[3]
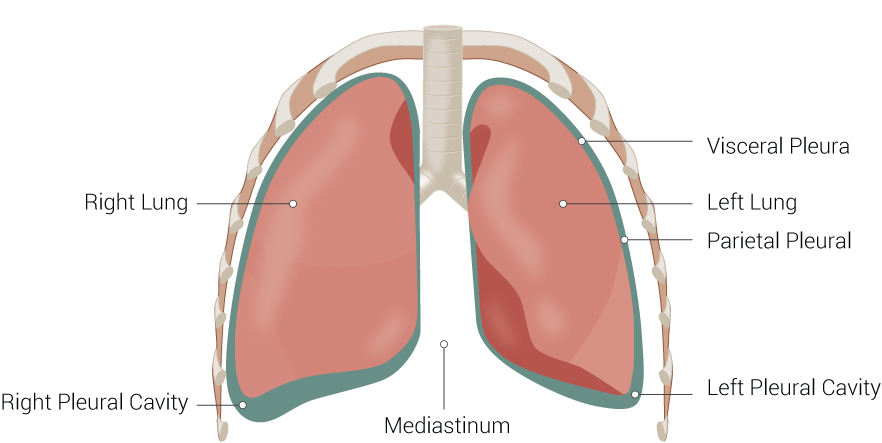
The lung divides into two lobes on the left and three lobes on the right, which are visible on gross anatomy.
Function
The lung mainly functions in two ways: conduction and respiration. As previously described, these functions can be examined in particular zones of the lung: conduction zone and respiratory zone. Conduction involves the warming and filtration of air, while respiration includes the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Respiration is highly dependent on the compliance of the lung and chest wall, the resistance of airways, and the rate of ventilation. Together, these components allow an A-a gradient to guide air appropriately into the lungs on inhalation and exhalation.
Compliance of the respiratory system describes the expandability of the lungs and chest wall. There are two types of compliance: dynamic and static. Dynamic compliance describes the compliance measured during breathing, which involves a combination of lung compliance and airway resistance. Static compliance describes pulmonary compliance when there is no airflow, like an inspiratory pause. Pressure-volume curves are common schemes to express the relationship of dynamic and static compliance where the slope is compliance.[14]
C = V/P
- C: Compliance (ml/mmHg)
- V: Volume (mL)
- P: Pressure (mm Hg)
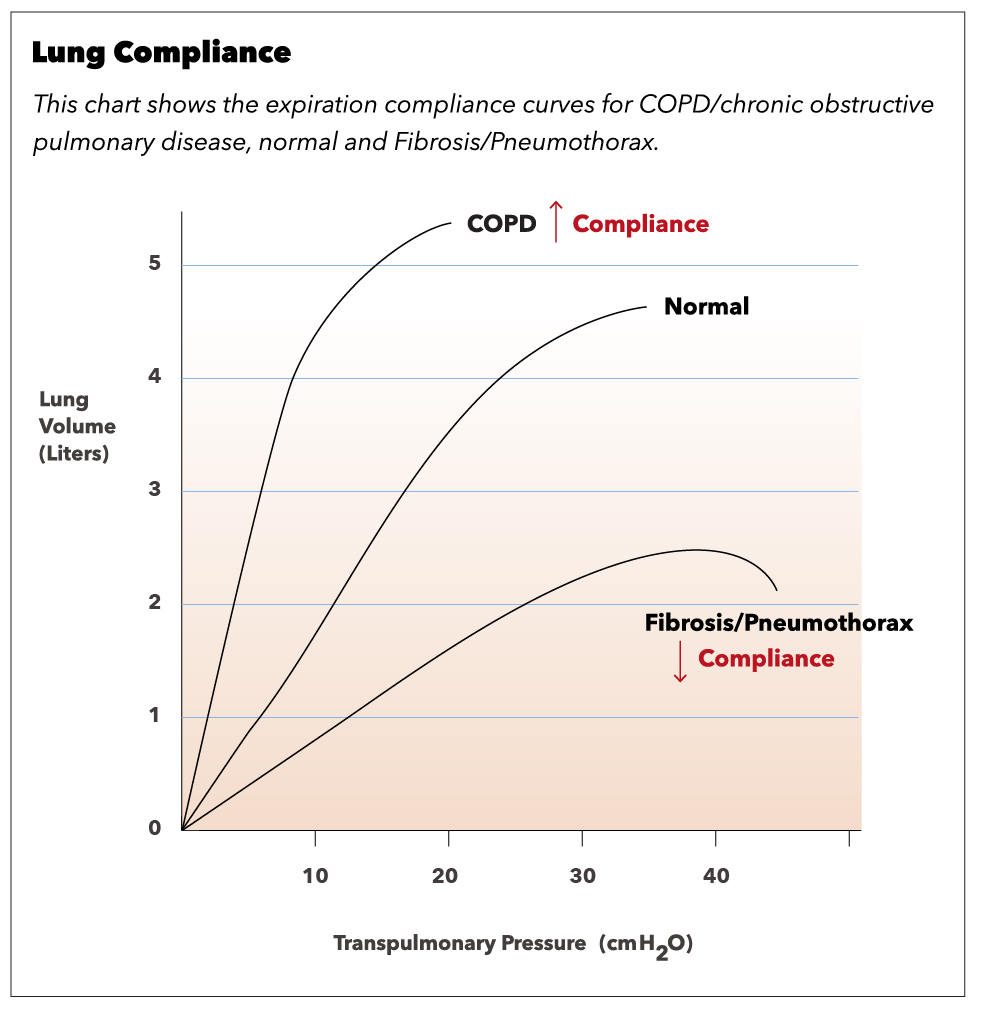
Lung compliance is the change in volume in the lungs for a given change in transpulmonary or transmural pressure. The transmural pressure (PTM) is the difference between intrapleural pressure( PA) and alveolar pressure (Pa), [PTM= PA – Pa]. If the intrapleural pressure is more negative, the lungs increase in volume to expand. However, if the intrapleural pressure is positive, the lungs will collapse, which decreases lung volume. During expiration, the lung volume is higher for a given intrapleural pressure, and, therefore, compliance is higher in expiration compared to inspiration. Lung compliance is inversely related to elastance, which is also known as elastic resistance or elastic recoil. So, a patient with low lung compliance will have a relatively stiff lung and, therefore, higher elastance.[15]
Two important factors of lung compliance are elastic fibers and surface tension. More elastic fibers in the tissue lead to ease in expandability and, therefore, compliance. Surface tension within the alveoli is decreased by the production of surfactant to prevent collapse. Compliance is more easily achieved by decreasing surface tension.
The lung and chest wall, together, form a combined compliance system. Independently each lung and chest wall measures higher compliance than the lung-chest wall system combined. In addition to lung compliance, the combined system factors in the opposing force of the chest wall muscles and diaphragm. These muscles provide the necessary pressure difference for air movement. The combined lung-chest wall system is at equilibrium (no inclination toward collapse or expansion) when lung volume is at functional residual capacity (FRC), which is the remaining lung volume after tidal volume is expired. The negative intrapleural pressure is set by the two opposing forces of the chest and lungs.[16]
Related Testing
Mechanical Ventilation: Pulmonary compliance is directly measurable in a mechanically ventilated patient. For accuracy, airway resistance is removed as a contributing factor by taking static measurements as opposed to dynamic. To determine static measurements, the examiner records end-expiratory alveolar pressure and end-inspiratory alveolar pressure. The tidal volume, change in lung volume, is divided by the change in pressure. After plotting these measurements, the slope reveals lung compliance. Measurement of compliance is useful when monitoring critically ill patients at the bedside.[17]
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a group of noninvasive tests that measure lung function. PFTs are not tests of diagnosis, but they help support a diagnosis by supplementing detailed history, physical exam findings, and laboratory results. To interpret and use PFT results, an understanding of lung compliance is necessary.[14][18]
Pathophysiology
Restrictive lung diseases - fibrosis and interstitial lung disease: In interstitial lung diseases, the lung and/or chest wall compliance has become decreased. Therefore there is an increased tendency for the lungs to collapse. Because of the restriction on lung expansion, there is also a reduced lung volume (low FVC and TLC). Since at the original FRC, the tendency to collapse is high, the lung-chest wall system seeks a lower FRC to balance the opposing forces. PFTs usually reveal in a high FEV1/FVC ratio. FEV1 is the volume of air forcefully expired in the first second.
Values of 80 percent (0.8) of the average are considered normal. Restrictive lung diseases include fibrosis and interstitial lung diseases (pneumoconiosis, sarcoidosis, etc.). Pulmonary mechanical issues can also lead to a restriction in lung expansion.
Restrictive lung disease can result from mechanical issues with peripheral hypoventilation, including poor muscular effort or structural dysfunction. Conditions like muscular dystrophy, polio, myasthenia gravis, and Guillain-barre syndrome can cause poor muscular effort. Muscular dystrophy reduces the ability of the lung to distend for unknown reasons, which reduces lung compliance. However, although there is an impact, respiratory muscle weakness or tension is not directly related to pulmonary compliance. Scoliosis or morbid obesity can also cause structural limitations.[23]
Obstructive lung disease: When there is an obstruction of airflow, the path of air becomes halted earlier than expected at high lung volumes. This condition leads to trapped air in the lungs. Compliance can be normal or increased. PFTs usually reveal a low FEV1/FVC ratio as FEV1 is reduced significantly more than FVC. Again, since at the original FRC, the tendency to collapse is high, the lung-chest wall system seeks a lower FRC to balance the opposing forces. Obstructive lung diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, and emphysema.[24]
- Asthmatic patients present with cough, wheeze, dyspnea, tachypnea, hypoxemia, and mucus plugging. Asthma is characterized by hypersensitive bronchi (a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction). Diagnosis can be made by spirometry and followed by a methacholine challenge.
- COPD categorizes into two conditions: chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
- Patients with chronic bronchitis are also known as blue bloaters. They present with wheezing, dyspnea, crackles, cyanosis, CO2 retention, and/or secondary polycythemia. There is usually a history of chronic productive cough because of hyperplasia and hypertrophy of glands secreting mucus in the bronchi.[16]
- Patients with emphysema are also known as pink puffers. A classic finding in these patients is a barrel-shaped chest, which is apparent on a chest X-ray. DCLO decreases due to the destruction of alveolar walls. The most common risk factor is smoking, which leads to a loss of elastic fibers and increased lung compliance. A common technique used to relieve symptoms is breathing with pursed lips to increase pressure in the airways and prevent collapse.[16]
There are cases of mixed obstructive and restrictive lung diseases where there is a premature formation of segments that restrict airflow. Also, there is low lung compliance, which, combined, leads to a decrease in FVC.
Clinical Significance
Pneumothorax: This condition characteristically demonstrates the accumulation of air in the intrapleural space. This leads to the equalization of intrapleural pressure with atmospheric pressure. As a result, the chest wall protrudes outward, and lungs collapse as this is the natural tendency without transmural pressure. The patient will commonly present with dyspnea, chest pain, uneven expansion of the chest, and diminished breath sound on the affected side. Without proper transmural pressure, lung-chest wall compliance is inoperable.[25]
Obesity results in low lung compliance with reduced functional residual capacity and expiratory reserve volume.[26]
Scoliosis decreases the chest wall and lung compliance that results in increased respiratory workload.
Aging is accompanied by a decrease in muscular strength and elastic recoil. Therefore, lung compliance increases and chest wall compliance decreases as age increases.[27]